blog
Schema Markup: The Shortcut to Standing Out in SERPs

Here’s a hard truth: great content isn’t enough anymore.
You could publish the most detailed guide in your niche… and still get buried on page two.
Why?
Because search engines don’t just need content. They need context.
That’s where schema markup comes in. When applied correctly, schema markup ensures your content isn’t just indexed but fully understood by search engines.
Schema is like SEO’s secret weapon. It tells Google exactly what your page is about so your content isn’t just indexed, it’s understood. And when Google understands your content, you win richer snippets, higher visibility, and more clicks.
In fact, research shows that pages using schema can see up to 30% more clicks than those without. That’s free traffic… without writing a single extra word.
In this guide, I’ll break down schema in plain English. You’ll learn what it is, why it matters, and how to implement it (step-by-step). I’ll also show you the biggest mistakes to avoid and a few advanced tricks to get ahead of the curve.
What Is Schema Markup?
If SEO is about speaking Google’s language, schema markup is the dictionary.
At its core, schema is structured data, an extra code you add to your web pages. This code doesn’t change how your content looks to users. Instead, it tells search engines what your content actually means.
Schema Defined in Simple Terms
Think of schema as a label. Without it, Google sees your page as plain text. With schema, Google knows:
- This is a recipe (not just a blog post).
- This number is a price (not just random text).
- This name is an author (not just a word on a page).
That extra context makes a huge difference in how your content shows up in search.
How Schema Helps Search Engines Understand Context
Search engines aren’t mind readers. Schema gives them clues. It bridges the gap between “what you wrote” and “what you meant.” The result? Better indexing and richer search results.
Schema.org and JSON-LD Basics
Schema markup follows guidelines from Schema.org, a project supported by Google, Bing, and Yahoo. The most common format today is JSON-LD. It’s lightweight, flexible, and recommended by Google itself.
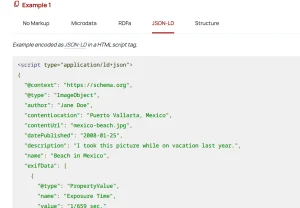
Image Source: Screenshot of a structured data markup example from Google’s documentation showing JSON-LD format.
So when you hear “schema markup,” think: a simple script in your site’s code that makes your content crystal clear to search engines.
Bottom line: Schema markup isn’t complicated. But it’s powerful. And it can change how your site appears in search overnight.
Why Schema Markup Matters for SEO
Here’s the truth: schema doesn’t directly boost your rankings. But it does improve how your content performs in search.
Think of it like this: backlinks and content get you in the race. Schema gives you the turbo engine.
Used thoughtfully, schema markup for SEO can lift CTR and engagement by making your listing more useful at a glance.
Direct and Indirect Ranking Signals
Google has said schema isn’t a direct ranking factor. But it influences metrics that are like click-through rate (CTR), dwell time, and engagement. When more users click your result and stick around, Google notices.
Rich Snippets and Higher CTR
Ever seen results with star ratings, FAQs, images, or prices listed under them? That’s schema at work. These “rich snippets” make your listing stand out from boring blue links. More visibility = more clicks. In fact, studies show schema can boost CTR by 20–30%.

Image Source: Created using Napkin AI.
Structured Data and Voice Search
Voice assistants (like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant) rely heavily on structured data. If your content has schema, it’s more likely to be pulled as a voice search answer. With voice search growing every year, that’s a huge edge.
Benefits of Schema Markup for SEO
So, why bother with schema markup? Simple: it gives your content more visibility, more clicks, and a better user experience.
Better Organic CTR
Schema makes your search listings pop. Instead of a plain blue link, your result can show star ratings, prices, FAQs, or event details. That visual boost draws the eye and earns more clicks. In fact, schema-powered results often enjoy 20–30% higher CTR compared to standard ones.
More Relevant Search Visibility
Without schema, Google can only guess what your page is about. With schema, it knows. That means your content appears for more accurate and relevant searches. Example: A recipe post without schema looks like any other blog. Add recipe schema, and suddenly your page shows cook time, calories, and reviews right in search.
Enhanced Mobile and Voice Experience
Mobile and voice searches are exploding. Schema makes your site more “readable” for both. When someone asks Alexa for the best Italian restaurant nearby, businesses with local schema are far more likely to surface in the answer.
Different Types of Schema Markup for SEO You Should Know
Schema isn’t one-size-fits-all. Different schema types serve different purposes. The good news? You don’t need them all. Just pick the ones that align with your business goals.
Article and Blog Schema
Running a blog? Article schema helps Google understand your post type (news, blog, or general article). It can also display your logo, publish date, and author in search results. That means more trust and higher clicks.
Product and Review Schema
For ecommerce, this one is gold. Product schema highlights prices, stock availability, and descriptions. Review schema adds star ratings. Together, they make your listing stand out in crowded SERPs.
Local Business Schema
If you own a brick-and-mortar store, restaurant, clinic, or gym, local business schema is a must. It signals your NAP (Name, Address, Phone) directly to search engines. Bonus: It boosts your chances of showing in Google’s local pack.
Local businesses can benefit by combining schema markup with our local SEO services to dominate map pack rankings.
FAQ and HowTo Schema
Want extra real estate in search results? FAQ schema adds collapsible questions and answers under your listing. HowTo schema works well for tutorials, showing step-by-step instructions right in the SERP.
Pairing schema-driven organic visibility with our PPC management services can maximize CTR across both paid and organic campaigns.
How to Implement Schema Markup
Schema sounds technical. But adding it to your site is easier than you think. You’ve got three main options:
Manual JSON-LD Approach
The cleanest way is to add schema using JSON-LD, Google’s recommended format. You simply copy a script (in JSON format) and paste it into your page’s <head> or body. Example: If you’re adding product schema, you’d include fields for name, price, and availability. It’s fast, flexible, and easy to edit.
Plugins and SaaS Tools
Not a coder? No problem. WordPress users can add schema with plugins like Yoast SEO, Rank Math, or Schema Pro. For bigger sites, SaaS platforms like Merkle’s Schema Generator or Google Tag Manager make it scalable. These tools do the heavy lifting so you don’t have to mess with code.
Yoast offers built-in schema support for WordPress users.
Validating Schema with Google Tools
Once your schema is live, test it. Google provides two free tools:
- Rich Results Test – shows if your schema is eligible for rich snippets.
- Schema Markup Validator – checks for errors or missing fields.
Validating ensures your schema is not just present, but working as intended.
Pro Tip: Start small – add one schema type, validate it, and then scale across your site.
Best Practices for Schema Markup for SEO
Adding schema is one thing. Doing it right is another. Follow these best practices to get maximum SEO value.
Stay Relevant and Accurate
Don’t force schema where it doesn’t belong. If you run a blog, don’t add product schema unless you’re actually selling something. Google is strict about this. Misuse can lead to manual penalties or lost rich snippets.
Combine Multiple Schema Types
One page can use more than one schema. For example, a blog post reviewing a product can have Article Schema + Product Schema + Review Schema. The key is to keep it logical and relevant to the page content.
Monitor and Update Regularly
Schema isn’t a “set it and forget it” deal. Prices change, events get canceled, businesses move addresses. If your schema stays outdated, Google may drop your eligibility for rich snippets. Use tools like Google Search Console to spot errors early.
Pro tip: Start with your most important pages (home, product, services, or blogs that drive traffic). Once those are optimized, expand schema site-wide.
Common Schema Mistakes to Avoid
Schema is powerful but only if you use it correctly. Mess it up, and you’ll lose the benefits (or worse, trigger penalties). Here are the biggest pitfalls:
Misusing or Overusing Schema
Don’t tag everything on your site with schema just for the sake of it. If your content doesn’t match the schema type, skip it. For example, adding recipe schema to a non-recipe blog post? That’s a fast way to lose Google’s trust.
Forgetting Validation Errors
Adding schema isn’t enough. You need to test and validate it. If your markup has errors or missing fields, it won’t qualify for rich snippets. Always run your code through Google’s Rich Results Test before going live.
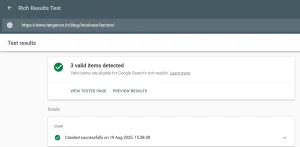
Image Source: Screenshot of a Google Rich Results Test.
Relying on Outdated Formats
Some sites still use microdata or RDFa formats. While they technically work, Google recommends JSON-LD. Stick with the modern standard for clean code and easier management.
Advanced Schema Strategies
Once you’ve nailed the basics, it’s time to take schema to the next level. Advanced tactics can give your site a competitive edge.
Nested Schema for Complex Pages
Some pages have multiple entities like a blog post that reviews a product. In this case, you can “nest” schema types. Example: Article Schema can contain Review Schema, which itself can include Product Schema. This layered approach gives Google deeper context, helping your page qualify for multiple rich features.
Leveraging SameAs for Entities
The sameAs property links your brand to other trusted sources, like your official social profiles or Wikipedia page. Example:
“sameAs”: [
“https://www.facebook.com/yourbrand”,
“https://www.linkedin.com/company/yourbrand”
]
This strengthens entity recognition and can increase your chances of appearing in knowledge panels.
Schema for Knowledge Panels and AI
Google’s Knowledge Graph and AI-powered search rely heavily on structured data. Adding schema for Organization, Person, or Event makes it easier for Google to build a knowledge panel for your brand. In a world moving toward AI-driven search results, this is pure gold.
The Bottom Line
Schema markup may feel like “extra SEO work,” but it’s actually a growth multiplier. It doesn’t replace great content or backlinks but it makes both work harder for you.
With the right schema, your pages stand out in search, attract more clicks, and deliver a better user experience. From star ratings to FAQs to local business details, structured data gives your content the visibility it deserves.
The best part? You don’t need to implement every schema type at once. Start with just one like FAQ or Product schema and build from there.
At Tangence, our SEO services help businesses stay ahead of algorithm updates, and schema markup is one of the most effective strategies we use.
Future-proof your SEO with schema. Partner with Tangence and get expert implementation that drives measurable results.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Does schema directly improve rankings?
No. Schema itself isn’t a direct ranking factor. But it improves your CTR, visibility, and engagement signals that Google does care about. That’s why sites with schema often outperform those without.
2. What’s the difference between schema and structured data?
“Structured data” is the broad term for any code that organizes information for search engines. “Schema” is a specific vocabulary (from Schema.org) used to mark up that data. In simple terms: schema = structured data format.
3. Is JSON-LD better than microdata?
Yes. Google recommends JSON-LD because it’s cleaner, easier to manage, and less likely to break your site’s design. Microdata still works, but it clutters your HTML. JSON-LD keeps everything neat in a script block.
4. Can schema markup cause SEO issues?
Only if you misuse it. For example, adding recipe schema to a non-recipe blog or using fake review stars can trigger penalties. Stick to relevant schema, validate it, and you’re safe.
5. How often should schema be updated?
Any time your content changes. If your business hours, prices, or events change, update the schema too. Outdated schema can disqualify you from rich snippets.
6. Which plugins/tools are best for schema?
For WordPress: Rank Math, Yoast SEO, and Schema Pro are solid. For non-WordPress sites, free tools like Merkle’s Schema Generator and Google Tag Manager work great.
7. Is schema markup useful for SaaS websites?
Absolutely. SaaS companies can use FAQ Schema, How To Schema, or Product Schema on feature pages. This makes listings more engaging and increases clicks even against strong competitors.




