blog
Page Speed Optimization: How Website Speed Impacts SEO in 2026

In 2026, website speed is no longer just a technical consideration, it is a decisive SEO factor. Users expect pages to load instantly, and search engines now evaluate performance as a core component of search visibility. This shift has made page speed optimization essential for any website that wants to compete in organic search results.
Google’s algorithms increasingly prioritize real user experience. Metrics like Core Web Vitals, mobile performance, and responsiveness directly influence how pages are crawled, indexed, and ranked. A slow website doesn’t just frustrate users; it wastes crawl budget, increases bounce rates, and sends negative engagement signals to search engines.
As competition grows across every niche, fast-loading websites gain a clear advantage. They retain users longer, convert better, and maintain ranking stability even as algorithms evolve. This guide explains how website speed impacts SEO in 2026, which performance metrics truly matter, common speed issues that hurt rankings, and proven strategies to optimize speed without compromising usability or design.
What Is Page Speed Optimization?
Page speed optimization is the process of improving how quickly a web page loads and becomes interactive for users. From an SEO perspective, it is not limited to reducing load time, it focuses on delivering meaningful content quickly, ensuring smooth interaction, and providing a stable visual experience.
It’s important to distinguish between page speed and site speed. Page speed measures the performance of a single URL, while site speed reflects the overall performance of a website. Google evaluates page-level performance when ranking individual URLs, making optimization at the page level critical.
Modern performance measurement relies on multiple milestones that represent different stages of user experience.
Difference Between Key Page Speed Metrics
| Metric | What It Measures | SEO Importance | Ideal Target |
|---|---|---|---|
| Load Time | Total time to load all page elements | Low (diagnostic only) | Under 3 seconds |
| TTFB | Server response time | Medium | Under 800 ms |
| FCP | First visible content | Medium | Under 1.8 seconds |
| LCP | Main content loading | High (Core Web Vital) | Under 2.5 seconds |
In 2026, Google relies heavily on real-user performance data collected through the Chrome User Experience Report. This means page speed optimization must work consistently across devices, networks, and locations, not just in lab tests.
How Website Speed Impacts SEO Rankings in 2026
Website speed influences SEO in both direct and indirect ways. While Google may not rank pages solely based on raw speed scores, performance strongly affects how search engines crawl, index, and evaluate user experience signals. Website speed is a core part of technical SEO, alongside crawlability, indexing efficiency, and site architecture, all of which are addressed through comprehensive technical SEO services.
Speed as a Ranking & Indexing Signal
Fast-loading pages allow search engines to:
- Crawl more pages efficiently within a limited crawl budget
- Index content faster after updates
- Reduce server strain during crawling
Slow websites, on the other hand, often experience delayed indexing and inconsistent rankings, especially for large or frequently updated sites.
Core Web Vitals & Search Visibility
Google has officially confirmed that page experience signals, including Core Web Vitals, play a role in ranking as outlined in its Page Experience documentation.
- LCP evaluates loading performance
- INP measures responsiveness and interactivity
- CLS tracks visual stability
Pages that consistently meet Core Web Vitals thresholds tend to outperform slower competitors in search results, particularly in competitive niches.
Behavioral SEO Signals & User Engagement
Website speed directly affects:
- Bounce rate
- Time on page
- Pages per session
- Conversion rates
When users abandon slow pages quickly, search engines interpret this as poor relevance or experience. Over time, these negative engagement signals can suppress rankings, even if the content itself is high quality.
Ultimately, faster websites create a positive feedback loop: better performance leads to better engagement, which strengthens SEO authority and ranking stability.
Page Speed Optimization for Mobile-First Indexing
Google’s mobile-first indexing means that the mobile version of your website is now the primary version used for crawling, indexing, and ranking. In 2026, this makes mobile page speed optimization more critical than ever, especially as mobile traffic dominates most industries.
Mobile users typically browse on slower networks, smaller screens, and less powerful devices. As a result, performance issues that may seem minor on desktop can severely impact mobile usability and SEO. A slow mobile experience often leads to higher bounce rates, reduced engagement, and lower search visibility. 
Image Source: Google PageSpeed Insights (Desktop vs Mobile performance report)
Common mobile-specific speed issues include:
- Heavy JavaScript frameworks that delay interactivity
- Large, uncompressed images not adapted for mobile screens
- Render-blocking CSS that slows above-the-fold content
- Excessive third-party scripts such as ads, trackers, and chat widgets
From an SEO standpoint, Google evaluates mobile speed using real-user data, not just simulated tests. This means your site must perform consistently across various devices and network conditions to maintain strong rankings.
Key Page Speed Metrics You Must Track in 2026
Tracking the right performance metrics is essential for effective page speed optimization. In 2026, Google evaluates website speed using a combination of Core Web Vitals and supporting performance indicators that reflect real user experience rather than isolated test results.
Core Web Vitals Metrics
According to Google’s Web.dev guidelines, Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) should occur within 2.5 seconds to deliver a good user experience.
| Metric | What It Measures | Good | Needs Improvement | Poor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCP | Loading performance | ≤ 2.5s | 2.5–4s | > 4s |
| INP | Interactivity | ≤ 200ms | 200–500ms | > 500ms |
| CLS | Visual stability | ≤ 0.1 | 0.1–0.25 | > 0.25 |
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- Measures how quickly the main content of a page becomes visible.
- A good LCP score indicates strong loading performance and user satisfaction.
- Target benchmark: under 2.5 seconds for most users.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP)
- Assesses how responsive a page is to user interactions such as clicks, taps, and keyboard inputs.
- Replaced First Input Delay (FID) as the primary interactivity metric.
- A low INP ensures smoother, frustration-free browsing.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
- Tracks unexpected layout movements during page load.
- High CLS leads to poor usability and accidental clicks.
- Stable layouts contribute to higher engagement and trust.
Supporting Performance Metrics
- Time to First Byte (TTFB)
Reflects server responsiveness and backend efficiency. - First Contentful Paint (FCP)
Indicates when users first see content on the screen. - Speed Index
Measures how quickly visible elements are populated during load.
Why These Metrics Matter for SEO
Google prioritizes field data collected from real users through the Chrome User Experience Report. This means consistent performance across devices, networks, and locations is more important than achieving perfect lab scores.
Monitoring these metrics allows you to diagnose bottlenecks, prioritize fixes, and align your website with Google’s performance expectations making them a non-negotiable part of any SEO strategy in 2026.
Tools to Measure Page Speed Optimization Accurately
Accurate measurement is the foundation of page speed optimization. Because Google evaluates both lab and field data, multiple tools are required for a complete analysis.
| Tool | Data Type | Best Used For | SEO Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| PageSpeed Insights | Field + Lab | Google ranking alignment | Core Web Vitals |
| Lighthouse | Lab | Debugging issues | Development |
| GTmetrix | Lab | Waterfall analysis | Asset optimization |
| WebPageTest | Lab | Advanced testing | Enterprise SEO |
| CrUX | Field | Real-user insights | Long-term tracking |
Use PageSpeed Insights and CrUX to understand SEO impact, and Lighthouse or GTmetrix to diagnose technical problems.
Common Page Speed Issues That Hurt SEO
Even well-designed websites can suffer from performance problems that quietly damage search visibility. In many cases, poor page speed optimization is the result of avoidable technical and structural issues rather than content quality.
Technical Performance Issues
- Unoptimized Images
- Large image files increase load time and delay Largest Contentful Paint (LCP).
- Lack of modern formats such as WebP or AVIF worsens performance.
- Excessive JavaScript
- Heavy JavaScript frameworks block rendering and delay interactivity.
- Poorly managed scripts increase Interaction to Next Paint (INP).
- Render-Blocking CSS and Scripts
- Resources that load before visible content delay First Contentful Paint (FCP).
- Common in poorly optimized themes and templates.
- No Caching Strategy
- Without browser or server-side caching, repeat visitors experience unnecessary delays.
- Increases server load and worsens user experience.
CMS-Specific Performance Problems
- Plugin Overload (Especially in WordPress)
- Too many plugins introduce redundant scripts and styles.
- Conflicting plugins often degrade performance metrics.
- Heavy Themes and Page Builders
- Over-designed themes add bloated CSS and JavaScript.
- Page builders often prioritize design flexibility over speed.
- Poor Media Management
- Uploading original image sizes without compression.
- Missing lazy loading configuration.
Server and Hosting Issues
- Slow Hosting Infrastructure
- Shared or low-quality hosting leads to high TTFB.
- Server delays impact every page on the site.
- No Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Users far from the server experience slower load times.
- Affects global SEO and international visibility.
- Inefficient Backend Processing
- Poor database optimization increases response time.
- Affects both crawling and real-user performance.
Addressing these issues is essential for maintaining strong rankings. Ignoring them not only weakens SEO but also limits the effectiveness of your content and marketing efforts.
Page Speed Optimization Best Practices for 2026
In 2026, effective page speed optimization requires a balanced approach, one that improves performance without compromising design, functionality, or user experience. Google prioritizes real-world usability over theoretical perfection, making sustainable optimization more important than chasing perfect scores.
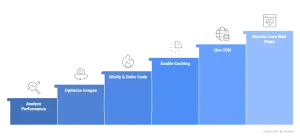
Image Source: Created using Napkin AI.
Front-End Optimization Techniques
- Optimize Images with Next-Gen Formats
- Use WebP or AVIF to reduce file size without quality loss.
- Serve responsive images tailored to device size.
- Compress all media before upload.
- Implement Lazy Loading
- Load images, videos, and iframes only when they enter the viewport.
- Reduces initial page load time and improves LCP.
- Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML
- Remove unnecessary spaces, comments, and unused code.
- Smaller files lead to faster downloads and rendering.
- Use Critical CSS
- Load only essential CSS for above-the-fold content first.
- Defer non-critical styles to avoid render-blocking delays.
Back-End Optimization Techniques
- Choose High-Performance Hosting
- Opt for cloud or managed hosting with modern server stacks.
- Reduces Time to First Byte (TTFB) significantly.
- Enable Server-Side Caching
- Use object caching, page caching, and opcode caching.
- Minimizes server processing time for repeat requests.
- Optimize Databases
- Remove unnecessary data, revisions, and unused tables.
- Improves backend response time and scalability.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Distributes content across global servers.
- Reduces latency and improves international SEO performance.
Advanced Optimization Strategies
- Adopt HTTP/3 and QUIC
- Faster, more reliable connections over unstable networks.
- Particularly beneficial for mobile users.
- Enable Brotli Compression
- Compresses files more efficiently than Gzip.
- Reduces transfer size and speeds up delivery.
- Reduce Third-Party Scripts
- Audit analytics, ads, and tracking tools regularly.
- Remove or defer non-essential scripts to improve INP.
- Use Edge Computing Where Possible
- Processes content closer to the user.
- Improves speed for dynamic and personalized content.
Successful optimization is not a one-time task. Regular audits, performance monitoring, and incremental improvements are essential to maintain SEO competitiveness in 2026.
Page Speed Optimization for Different Website Types
Page speed optimization is not a one-size-fits-all process. Different website types face unique performance challenges, and optimization strategies must align with user intent, content structure, and functionality requirements.
| Website Type | Primary Speed Focus | Key Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| Blog | Text rendering | Lightweight themes |
| eCommerce | Product images | Image optimization |
| Service Site | Landing pages | Minify CSS/JS |
| Enterprise | Crawl budget | CDN + caching |
| SaaS | Interactivity | Reduce JS payload |
Blogs and Content-Driven Websites
- Prioritize fast text rendering and lightweight layouts.
- Optimize featured images and inline media.
- Reduce third-party scripts such as ads and embedded widgets.
- Faster loading improves dwell time and content consumption.
eCommerce Websites
- Optimize product images and category pages for LCP.
- Implement efficient caching for product listings.
- Reduce script-heavy elements like sliders and pop-ups.
- Speed directly impacts conversion rates and cart abandonment.
Service-Based Business Websites
- Focus on fast-loading landing pages and contact forms.
- Minimize page builder bloat.
- Ensure mobile speed is optimized for local search intent.
- Improves lead generation and trust signals.
Enterprise and Large-Scale Websites
- Manage crawl budget with efficient server responses.
- Use CDNs and edge caching aggressively.
- Optimize JavaScript execution across thousands of pages.
- Performance consistency is critical for ranking stability.
SaaS and Web Applications
- Optimize application shell loading.
- Reduce initial JavaScript payload.
- Improve interactivity for logged-in users.
- Enhances both SEO visibility and user retention.
Aligning page speed optimization with website type ensures performance improvements translate directly into SEO and business outcomes.
How Page Speed Optimization Improves Conversions & Revenue
Page speed optimization directly influences conversions. Faster websites reduce friction, increase engagement, and build trust. Users are more likely to complete actions whether signing up, contacting a business, or making a purchase, when pages load quickly.
Improved speed lowers bounce rates, increases pages per session, and strengthens behavioral signals that support SEO performance. By aligning SEO with conversion rate optimization, speed improvements ensure that traffic not only arrives but converts.
What Google Really Rewards in 2026
In 2026, Google’s approach to page speed optimization is more nuanced than simply rewarding the fastest websites. Search engines prioritize consistent, real-world performance over isolated lab test scores.
One of the biggest misconceptions in SEO is the pursuit of a perfect “100/100” speed score. While performance tools are valuable, Google relies primarily on field data, how real users experience your website across different devices, locations, and network conditions.
What Google actually rewards includes:
- Consistency over perfection
Pages that perform reliably well for most users outperform those with occasional spikes or drops. - Balanced optimization
Speed improvements should not break usability, design, or functionality. - User-centric performance
Fast rendering of meaningful content matters more than loading background elements instantly. - Stable experiences
Minimal layout shifts and smooth interactivity build trust and reduce frustration.
Websites that align speed optimization with user intent, content relevance, and technical stability tend to see better long-term ranking results. Google’s algorithms increasingly favor pages that deliver value quickly, without unnecessary friction or delays.
In short, sustainable page speed optimization is about creating dependable, user-first experiences and not chasing vanity metrics.
Conclusion
In 2026, page speed optimization is a long-term SEO investment that directly impacts rankings, engagement, and revenue. Fast websites crawl better, rank more consistently, and convert users more effectively. Speed enables content to perform at its best and protects search visibility as algorithms evolve.
Businesses looking to improve search visibility, performance, and conversions can benefit from expert-led SEO services at Tangence that combine speed optimization with long-term growth strategies.
In a competitive digital landscape, optimizing page speed is no longer optional. It is essential for future-proof SEO success.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is page speed optimization in SEO?
It is the process of improving page loading and usability to enhance rankings and user experience.
2. How fast should a website load for SEO in 2026?
Ideally, main content should load within 2–3 seconds.
3. Does page speed directly affect rankings?
Yes, through page experience signals and user behavior.
4. What is a good Core Web Vitals score?
LCP under 2.5s, INP under 200ms, CLS below 0.1.
5. Can I improve speed without redesigning my site?
Yes, through caching, image optimization, and script reduction.
6. Is page speed optimization ongoing?
Yes, regular monitoring is required as sites evolve.
7. Which matters more: content or speed?
Both matter, but speed often differentiates competing content.